PANCHAKSHARI S PROFESSIONAL ACADEMY PVT LTD Your Lifelong Knowledge Partner...
|
|
|
- Brian Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test ID :095 Depriciation Instruction for Qusetion 1 To 50 MCQ Qn.1) A firm acquired machinery on 1st July, 2012 at a cost of Rs. 45,000 and spent Rs. 5,000 for its installation. The firm writes off depreciation at 10% per annum on diminishing balance method. The books are closed on 31st March every year. Depreciation for the year ended 31st March, 2012 & 31st March, 2013 will be Rs...&Rs A. 3,750 & 5,000 B. 4,625 & 3,750 C. 3,750 & 4,625 D. 5,000 & 3,750 Qn.2) Under which of following method depreciation is charged uniformly? A. Insurance policy method C. Depreciation fund method Qn.3) Reduction in the value of assets due to its continuous use is treated as A. loss B. profit C. appreciation D. depreciation Qn.4) Depreciation method that does not result in decreasing charges is- A. Sinking Fund method B. Double digit method C. Written down method D. Sum years digit method Qn.5) Hi-Fi Ltd. acquired machinery on 1st January, 2012 at a cost of Rs. 36,000 and spent Rs. 4,000 for its installation. The firm writes off depreciation at 10% p.a. on WDV basis. The books are closed on 31st December. Closing balance of machinery account for 1st & 2nd year will be Rs...&Rs... A. 32,400,29,160 B. 36,000,36,000 C. 32,400,36,000 D. 36,000,32,400 Qn.6)A machine of Rs 3,000 was sold for Rs 4,200. Depreciation provision to date was Rs 400 and commission paid to selling agent was Rs 420 and wages paid to workers for removing the machine was Rs 30. Profit on sale of machine will be : A. Rs 1,200 B. Rs 1,000 C. Rs 1,150 D. None of these Qn.7)Which method of depreciation is suitable when expenditure on repairs and maintenance, increases as the machine grows old? A. Reducing balance method B. Straight line method C. Machine hour rate method D. Sinking fund Method. Qn.8)Sangam Trading Co. started business by purchasing one machinery on 1st Jan costing Rs and spent Rs on its erection. On 30th June 2005 additional machinery costing Rs was purchased. Company provides depreciation every year ending on 30th 10% p. a. what is the amount of depreciation to be charged in the first year. A B C D Qn.9) H ltd purchased a machinery on April 01, 2000 for Rs. 3,00,000. It is estimated that the machinery will have a useful life of 5 years after which it will have no salvage value. If the company follows sum-of-theyears-digits method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation charged during the year was A. Rs. 100,000 B. Rs. 80,000 C. Rs. 60,000 D. Rs. 20,000 Qn.10) Which of the following is / are the important charac teristic of depreciation? A. Depreciation is a process of allocation of fu ture cost. B. Depreciation is caused due to physical factors and functional factors
2 C. Total depreciation can exceed its depreciable value or original cost Qn.11)C Ltd. acquired a machine on 1st January, 2010 at a cost of Rs. 14,000 and spent Rs. 1,000 on its installa tion. The firm writes off depreciation at 10% p.a. of closed on31st December every year. On 31st May, 2013 ma chine sold for Rs. 8,000. Profit/Loss on sale =? A. Profit - Rs. 2,275 B. Loss - Rs. 2,275 C. Profit - Rs. 1,875 D. Loss - Rs. 1,875 Qn.12)If an asset is bought on for Rs and is expected to be sold on for Rs what would be its annual depreciation. A. Rs. 500 B. Rs. 600 C. Rs D. Rs Qn.13)Which of the following is/are not the important characteristic of depreciation? A. Total depreciation can exceed its depreciable value or original cost B. Depreciation is calculated in respect of fixed assets only C. Depreciation is always computed in a system atic and rational manner Qn.14)A machine was purchased for Rs 50,000. Installation expenses amounted to Rs 2,000 wages of Rs 4,000 were paid on installation. The scrap value at the end of its useful life of 10 years is Rs 6,000.Repairs of Rs 6,000 was made after6 months from the date of purchase. Calculate depreciation A. Rs 5,600 B. Rs 4,800 C. Rs 5,000 D. None Qn.15)In the year , C ltd purchased a new machine and made the following payments in relation to it: Rs Rs Cost as per supplier s list 5,20,000 Less: Agreed discount 50,000 4,70000 Delivery charges 10,000 Erection charges 20,000 Annual maintenance 30,000 charges Additional components to 40,000 increase capacity of the machine Annual insurance 5,000 premium The cost of the machine is A. Rs. 540,000 B. Rs. 545,000 C. Rs. 470,000 D. Rs. 550,000 Qn.16)On April 01, 2004 the debit balance of the machinery account of A ltd was Rs. 5,67,000. The machine was purchased on April 01, The company charged depreciation at the rate of 10% per annum under diminishing balance method. Depreciation provided in = A. Rs. 56,700 B. Rs. 63,000 C. Rs. 70,000 D. Rs. 77,778 Qn.17)Original cost = Rs. 7,50,000. Installation charges =1,00,000, Salvage value = 50,000. Depreciation for 3rd year by units of production Method, if units produced in 3rd year was 40,000 and total estimated production 2,00,000. A. Rs. 1,20,000 B. Rs. 1,80,000 C. Rs. 1,60,000 D. Rs. 2,00,000 Qn.18)Z Ltd. acquired machinery on 1st January, 2011 at a cost of Rs. 72,000 and spent Rs. 8,000 for its installa tion. The firm writes off depreciation at 10% p.a. on closed on 31st December every year. Depreciation for 1st & 2nd year as per fixed installment method will be Rs... A. 6,000,6,000 B. 8,000,8,000 C. 8,000,7,200 D. 6,000,8,000 Qn.19)
3 A machine is purchased for Rs Expenses incurred for the cartage and installation Rs The residual value at the end of its expected useful life of 4 years is estimated at Rs Calculate the amount of depreciation for the first year ending on 31st March 2002, on SLM basis If the machined was purchased on 1st oct A. Rs B. Rs C. Rs D Qn.20)N Ltd. purchased a machinery on April 1, 2008 for Rs. 6,00,000. It is estimated that the machinery will have a useful life of 5 years after which it will have no salvage value. If the company follows sum of year digit method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation charged during the year was... A. Rs. 40,000 B. Rs. 1,20,000 C. Rs. 1,90,000 D. Rs. 2,00,000 Qn.21)Depreciation on machine sold up to in year will be Rs.... A. Rs. 16,560 B. Rs. 3,240 C. Rs. 11,200 D. Rs. 7,900 Qn.22)Original cost=rs. 12,00,000. Salvage value = 2,00,000. Useful Life = 10 years. Annual depreciation =? and rate of depreciation =? A. Rs. 1,00,000 & 8.33% B. Rs. 1,00,000 & 10%. C. Rs. 1,20,000 & 12% D. Rs. 1,20,000 & 8.33% Qn.23)Interest for the year ended 31st March, 2011 =? A. 1,05,000 B. 71,007 C. 89,115 Qn.24)Depreciation to be provided for each year =? A. 2,63,463 B. 2,48,463 C. 2,33,463 D. 2,18,463 Qn.25)For which of the following Inventory system of depreciation can be applied? A. Animals B. Loose tools C. Jars & bottles Qn.26) Original cost = Rs. 88,200. Salvage value = Rs. 4,200. Useful Life = 3 years. Depreciation rate =? A % B % C % Qn.27)Under which of following method depreciation charged does not decline? A. Insurance policy method C. Depreciation fund method Qn.28)Manan Printers. Mumbai, purchased a furniture on for Rs In the same year on another furniture costing Rs was purchased. Find out the amount of 10% on original cost and balance to be c/f in the next year on 1st Jan. 05 A and B and 5000 C and D and 6000 Qn.29)Z Ltd. acquired machinery on 1st January, 2011 at a cost of Rs. 72,000 and spent Rs. 8,000 for its installa tion. The firm writes off depreciation at 10% p.a. on closed on 31st December every year. Closing balance of ma chinery account for 1st & 2nd year as per fixed installment method will be Rs... A. 72,000,64,000 B. 74,000,66,000 C. 74,000, 72,000
4 D. 74,000,66,000 Qn.30)Which of the following is/are, cannot be treated as advantage of fixed installment method of charging depreciation? A. It is a simple and easy method. B. It takes into account the effective utilization of the asset. C. This method can be applied where asset gets depreciated because of efflux ion of time like furniture, equipment's, patents, leasehold etc. Qn.31)Which of the following is/ are the objectives of pro viding depreciation? A. To make provision for receivables B. To derive maximum tax benefit for excise duty by taking Cenvat credit. C. To present true financial position Qn.32)The net cost of new asset is and depreciation is charged on WDV 10% p.a. The next year depreciation is charged on the amount of A B C D Qn.33)Depreciation to be provided for each year =? A. 16, B. 14, C. 6, Qn.34)M/s NZ &Co. purchased a machine for Rs. 10,00,000. Estimated useful life and scrap value were 10 years and Rs. 1,20,000 respectively. The machine was put to use on If the company follows sum of year digit method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation charged during the year was... &... A. 64,000 & 48,000 B. 48,000 & 64,000 C. 1,12,000 & 1,28,000 D. 1,28,000 & 1,12,000 Qn.35)A new machine costing Rs. 1,00,000 was purchased by a company on 1st April, Its useful life is estimated to be 5 years and scrap value at Rs. 10,000. The production hours for the next 5 years is as follows: Year Hours , , , ,000 Depreciation for year =? A. 25,000 B. 15,000 C. 12,500 D. 6,250 Qn.36)Under sinking fund method of depreciation any surplus in sinking fund A/c is transferred to A. Capital Reserve A/c B. General Reserve A/c C. Reserve Capital A/c D. Profit and Loss A/c Qn.37)On April 01, 2004 the debit balance of the machinery account of A ltd was Rs. 5,67,000. The machine was purchased on April 01, The company charged depreciation at the rate of 10% per annum under diminishing balance method. Cost of machinery on = A. Rs. 567,000 B. Rs. 630,000 C. Rs. 700,000 D. Rs. 777,778 Qn.38) method, a fixed proportion of the original cost of the asset is written off each year so that asset account may be reduced to its residual value at the end of its estimated economic useful life. A. Fixed installment method B. Sum of year digit method C. Double decline method Qn.39)Balance of lease account for the year ended 31st March, 2011 =? A. 6,36,537 B. 5,07,189 C. 3,59,733 D. 1,91,633
5 Qn.40)Sinking Fund Investment Account balance for the year ended 31st March, 2010 =? A. 14,817 B. 31,412 C. Nil Qn.41)Depreciation is accounted for A. increase the profit B. reduce the profit C. present incorrect state of affairs D. None of these Qn.42)Where the life of the asset is uncertain... method of depreciation is applied. A. Depletion B. Machine hour rate C. Inventory system of depreciation D. Sum of years digit Qn.43)...is a method of accelerated depreciation that allocates larger amounts of depreciation as an expense during the earlier years of the life of an asset. A. Annuity method B. Inventory system of depreciation C. Sum of years digit method Qn.44)Amortization refers to writing off: D. General Reserve Qn.47)Obsolescence means decline in the value due to : A. Fall in the market price B. Physical wear and tear C. Efflux of time D. Innovations and inventions Qn.48)Under which of following method depreciation charged does not decline? A. Diminishing balance method C. Double decline method Qn.49)Life of an asset is 5 years, Purchase cost - Rs. 5,70,000, Installation charges - Rs. 30,000 Depreciation as per sum of years digit method for 4th year =? A. 1,60,000 B. 40,000 C. 2,00,000 D. 80,000 Qn.50)Under sum of year digit method depreciation year by year... A. Increases B. Decreases C. Remains constant D. None of above A. Depleting assets B. Wasting assets C. Intangible assets D. Fictitious assets Qn.45)Depreciation fund method is also known as... A. Redemption fund method B. Amortization fund method C. Sinking fund method Qn.46)In the case of downward revaluation of an asset which is for the first time revalued, the account to be debited is A. Fixed Asset B. Revaluation Reserve C. Profit and Loss account
The cost of this asset includes the purchase price, plus any taxes, commissions, and other amounts paid to make the asset ready for use.
 Accounting Fundamentals Lesson 7 7.0 Long-Term Assets Plant Assets, are long-lived assets that are tangible. The cost of this asset includes the purchase price, plus any taxes, commissions, and other amounts
Accounting Fundamentals Lesson 7 7.0 Long-Term Assets Plant Assets, are long-lived assets that are tangible. The cost of this asset includes the purchase price, plus any taxes, commissions, and other amounts
Accounting for tangible fixed Assets
 Accounting for tangible fixed Assets Fixed assets are used (not consumed) in operations of a business provide benefits beyond the current accounting period Fixed assets are either acquired or self constructed
Accounting for tangible fixed Assets Fixed assets are used (not consumed) in operations of a business provide benefits beyond the current accounting period Fixed assets are either acquired or self constructed
Copyright 2009 The Learning House, Inc. Fixed and Intangible Assets Page 1 of 13
 Copyright 2009 The Learning House, Inc. Fixed and Intangible Assets Page 1 of 13 Introduction This lesson focuses on the long-term assets used to operate a company. These assets can be grouped into fixed
Copyright 2009 The Learning House, Inc. Fixed and Intangible Assets Page 1 of 13 Introduction This lesson focuses on the long-term assets used to operate a company. These assets can be grouped into fixed
Chapter 08 - Long-Term Assets. Chapter Outline
 Section 1 Plant Assets I. Cost Determination Plant assets are tangible assets used in a company's operations that have a useful life of more than one accounting period. Consistent with cost principle,
Section 1 Plant Assets I. Cost Determination Plant assets are tangible assets used in a company's operations that have a useful life of more than one accounting period. Consistent with cost principle,
ILLUSTRATION 11-1 PATTERNS OF BOOK VALUE OVER LIFE OF ASSET
 ILLUSTRATION 11-1 PATTERNS OF BOOK VALUE OVER LIFE OF ASSET $ Cost of asset N PR: Book value activity methods Depreciable cost SL: Book value straight line Salvage value AC: Book value accelerated S E
ILLUSTRATION 11-1 PATTERNS OF BOOK VALUE OVER LIFE OF ASSET $ Cost of asset N PR: Book value activity methods Depreciable cost SL: Book value straight line Salvage value AC: Book value accelerated S E
Acquisition cost Purchase price plus all expenditures needed to prepare the asset for its intended use
 CAPITAL ASSETS Issues to consider: Compute initial acquisition cost Account for subsequent costs Allocate cost to periods benefited Record disposal Acquisition cost Purchase price plus all expenditures
CAPITAL ASSETS Issues to consider: Compute initial acquisition cost Account for subsequent costs Allocate cost to periods benefited Record disposal Acquisition cost Purchase price plus all expenditures
Accounting for Plant Assets and Depreciation
 Ch16 Accounting for Plant Assets and Depreciation 1 Understanding PPE Acquisition of PPE (cost) Depreciation of PPE Revenue expenditure vs. capital expenditure Disposition of PPE (sale, trade, and discard)
Ch16 Accounting for Plant Assets and Depreciation 1 Understanding PPE Acquisition of PPE (cost) Depreciation of PPE Revenue expenditure vs. capital expenditure Disposition of PPE (sale, trade, and discard)
5. The cost of buildings includes all necessary costs related to the purchase or construction
 CHAPTER REVIEW Plant Assets 1. (S.O. 1) Plant assets are tangible resources that are used in the operations of a business and are not intended for sale to customers. Plant assets are subdivided into four
CHAPTER REVIEW Plant Assets 1. (S.O. 1) Plant assets are tangible resources that are used in the operations of a business and are not intended for sale to customers. Plant assets are subdivided into four
Intermediate Accounting
 Intermediate Accounting 11-1 Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara 11 Depreciation, Impairments, and Depletion Intermediate Accounting 14th Edition 11-2 Kieso, Weygandt, and Warfield
Intermediate Accounting 11-1 Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara 11 Depreciation, Impairments, and Depletion Intermediate Accounting 14th Edition 11-2 Kieso, Weygandt, and Warfield
Paper 1: Accounting. Accounting Standards. Contents: AS 6 AS 10 As 9. CA Shruthi BN
 Paper 1: Accounting Accounting Standards Contents: CA Shruthi BN AS 6 AS 10 As 9 AS 6 Depreciation Accounting DEPRECIATION Meaning 2 It is a measure of wearing out, consumption or other loss of value of
Paper 1: Accounting Accounting Standards Contents: CA Shruthi BN AS 6 AS 10 As 9 AS 6 Depreciation Accounting DEPRECIATION Meaning 2 It is a measure of wearing out, consumption or other loss of value of
CHAPTER 9. Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets 6, 7, 8, 24, 25, 26 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 11, , 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22
 CHAPTER 9 Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE Study Objectives Questions Brief Exercises Do It! Exercises A Problems B Problems 1. Describe how the cost
CHAPTER 9 Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE Study Objectives Questions Brief Exercises Do It! Exercises A Problems B Problems 1. Describe how the cost
The Cost Principle. Plant Assets. Intangible Assets. Natural Resources. Depreciation. Amortization. Depletion. Chapter 9
 Plant Assets Natural Resources Intangible Assets Depreciation Depletion Amortization Chapter 9 2 Held for use in business Full cost includes several expenditures Last several years Can be sold or traded
Plant Assets Natural Resources Intangible Assets Depreciation Depletion Amortization Chapter 9 2 Held for use in business Full cost includes several expenditures Last several years Can be sold or traded
Fill-in-the-Blank Equations. Exercises
 Chapter 9 Long-Term Assets: Fixed and Intangible Study Guide Solutions 1. Residual value 2. Useful life 3. Straight-line rate 4. Total estimated units of activity 5. Straight-line rate 6. Depletion rate
Chapter 9 Long-Term Assets: Fixed and Intangible Study Guide Solutions 1. Residual value 2. Useful life 3. Straight-line rate 4. Total estimated units of activity 5. Straight-line rate 6. Depletion rate
CHAPTER 9 LONG-LIVED ASSETS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY
 CHAPTER 9 LONG-LIVED ASSETS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 17. 2 K 33. 2 C 49. 3 K 65.
CHAPTER 9 LONG-LIVED ASSETS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 17. 2 K 33. 2 C 49. 3 K 65.
Fill-in-the-Blank Equations. Exercises
 Chapter 10 Fixed Assets and Intangible Assets Study Guide Solutions 1. Residual value 2. Useful life 3. Straight-line rate 4. Total units of output 5. Straight-line rate 6. Depletion rate 7. Fixed asset
Chapter 10 Fixed Assets and Intangible Assets Study Guide Solutions 1. Residual value 2. Useful life 3. Straight-line rate 4. Total units of output 5. Straight-line rate 6. Depletion rate 7. Fixed asset
Chapter 11 Investments in Noncurrent Operating Assets Utilization and Retirement
 Chapter 11 Investments in Noncurrent Operating Assets Utilization and Retirement 1. The annual depreciation expense 2. The depletion of natural resources 3. The changes in estimates and methods in the
Chapter 11 Investments in Noncurrent Operating Assets Utilization and Retirement 1. The annual depreciation expense 2. The depletion of natural resources 3. The changes in estimates and methods in the
Depreciation. Dr. M. S. Memon. Mehran UET, Jamshoro, Pakistan. Department of Industrial Engineering and Management
 Depreciation Dr. M. S. Memon Department of Industrial Engineering and Management Mehran UET, Jamshoro, Pakistan https://msmemon.wordpress.com/scmlab/ Introduction Any equipment which is purchased today
Depreciation Dr. M. S. Memon Department of Industrial Engineering and Management Mehran UET, Jamshoro, Pakistan https://msmemon.wordpress.com/scmlab/ Introduction Any equipment which is purchased today
CHAPTER 6 - Accounting for Long-Term Operational Assets
 CHAPTER 6 - Accounting for Long-Term Operational Assets ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Long-term operational assets are those assets that are used by a business to generate revenue. In contrast, investments are
CHAPTER 6 - Accounting for Long-Term Operational Assets ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Long-term operational assets are those assets that are used by a business to generate revenue. In contrast, investments are
Chapter 9 Question Review 1
 Chapter 9 Question Review 1 Chapter 9 Questions Multiple Choice 1. The calculation of depreciation using the declining-balance method a. ignores salvage value in determining the amount to which a constant
Chapter 9 Question Review 1 Chapter 9 Questions Multiple Choice 1. The calculation of depreciation using the declining-balance method a. ignores salvage value in determining the amount to which a constant
EXERCISES. a. Yes. All expenditures incurred for the purpose of making the land suitable for its intended use should be debited to the land account.
 EXERCISES Ex. 9 1 a. New printing press: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 b. Used printing press: 7, 8, 9, 10 Ex. 9 2 a. Yes. All expenditures incurred for the purpose of making the land suitable for its intended use should
EXERCISES Ex. 9 1 a. New printing press: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 b. Used printing press: 7, 8, 9, 10 Ex. 9 2 a. Yes. All expenditures incurred for the purpose of making the land suitable for its intended use should
A Comparative Study on Depreciation as Per Companies Act and Income Tax Act in Indian Context
 A Comparative Study on as Per Companies Act and Income Tax Act in Indian Context CA. Poorvee Malde Visiting Lecturer Shri G. H. G. Commerce and Shri D. D. Nagda B.B.A. College, Jamnagar. Email: poorvee.malde@oshwaleducationtrust.org
A Comparative Study on as Per Companies Act and Income Tax Act in Indian Context CA. Poorvee Malde Visiting Lecturer Shri G. H. G. Commerce and Shri D. D. Nagda B.B.A. College, Jamnagar. Email: poorvee.malde@oshwaleducationtrust.org
Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Non-current Assets. Horngren, Best, Fraser, Willett: Accounting 6e 2010 Pearson Australia
 PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 11 Non-Current Assets: Property, Plant and Equipment, and Intangibles Learning Objectives 1. Measure the cost of a non-current asset 2. Account for depreciation 3. Select
PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 11 Non-Current Assets: Property, Plant and Equipment, and Intangibles Learning Objectives 1. Measure the cost of a non-current asset 2. Account for depreciation 3. Select
Chapter 9: Long-Lived Assets and Cost Allocation
 1 Chapter 9: Long-Lived Assets and Cost Allocation 2 Capitalize vs Expense Revenue Expenditures Merely maintain a given level of services Should be Expensed Debit Expense Capital Expenditures Provide future
1 Chapter 9: Long-Lived Assets and Cost Allocation 2 Capitalize vs Expense Revenue Expenditures Merely maintain a given level of services Should be Expensed Debit Expense Capital Expenditures Provide future
ACCOUNTING - CLUTCH CH. 8 - LONG LIVED ASSETS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INITIAL COST OF LONG-LIVED (PLANT) ASSETS Plant Assets include,,, and RULE: Initial cost includes the price plus all expenditures to make an asset When recording the initial
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INITIAL COST OF LONG-LIVED (PLANT) ASSETS Plant Assets include,,, and RULE: Initial cost includes the price plus all expenditures to make an asset When recording the initial
Chapter 9 - REPORTING AND ANALYZING LONG-LIVED ASSETS
 Revised Summer 2018 Chapter 9 Review 1 Chapter 9 - REPORTING AND ANALYZING LONG-LIVED ASSETS LO 1: Explain the accounting for plant asset expenditures. Plant Assets (Also known as Property, Plant, and
Revised Summer 2018 Chapter 9 Review 1 Chapter 9 - REPORTING AND ANALYZING LONG-LIVED ASSETS LO 1: Explain the accounting for plant asset expenditures. Plant Assets (Also known as Property, Plant, and
A 1: It( SPECIFIC ITEMS SECTION 3061 property, plant and equipment. Additional Resources. Page 1 of6. Knotia - CICA Handbook - Accounting A2-14
 '" Knotia - CICA Handbook - Accounting»Accounting»Accounting Handbook»Accounting Standards»Specific items [Sections 3000-3870]»3061 - Property, Plant and Eauipment Page 1 of6 A 1: It( A2-14 SPECIFIC ITEMS
'" Knotia - CICA Handbook - Accounting»Accounting»Accounting Handbook»Accounting Standards»Specific items [Sections 3000-3870]»3061 - Property, Plant and Eauipment Page 1 of6 A 1: It( A2-14 SPECIFIC ITEMS
Example 1: Separating lease/non-lease elements
 List of Examples N. Title Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Example 6 Example 7 Example 8 Example 9 Example 1 Example 11 Example 12 Example 13 Example 14 Separating the lease element from
List of Examples N. Title Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Example 6 Example 7 Example 8 Example 9 Example 1 Example 11 Example 12 Example 13 Example 14 Separating the lease element from
Week11, Chap 8 Accounting 1A, Financial Accounting
 Week11, Chap 8 Accounting 1A, Financial Accounting Reporting and Interpreting Property, Plant, and Equipment;Natural Resources; and Intangibles Instructor: Michael Booth Understanding The Business Insufficient
Week11, Chap 8 Accounting 1A, Financial Accounting Reporting and Interpreting Property, Plant, and Equipment;Natural Resources; and Intangibles Instructor: Michael Booth Understanding The Business Insufficient
University of Nizwa / Dept. of Architecture / ARCH 506: Building Specification & Estimation / VALUATION / Ravishankar. KR / 5, January 2011.
 Property Valuation Building Estimation and Costing Building Estimation and Costing Building Estimation and Costing is a vital part of Civil Engineering. No project can begin without the total Building
Property Valuation Building Estimation and Costing Building Estimation and Costing Building Estimation and Costing is a vital part of Civil Engineering. No project can begin without the total Building
Chapter 8. Accounting for Long-Term Assets
 Chapter 8 Accounting for Long-Term Assets C 1 Plant Assets Tangible in Nature Actively Used in Operations Expected to Benefit Future Periods Called Property, Plant, & Equipment 8-2 C 1 Plant Assets Decline
Chapter 8 Accounting for Long-Term Assets C 1 Plant Assets Tangible in Nature Actively Used in Operations Expected to Benefit Future Periods Called Property, Plant, & Equipment 8-2 C 1 Plant Assets Decline
Prepared by: Alex Socratous For My High School Students
 Prepared by: Alex Socratous For My High School Students CHAPTER 2 CAPITAL ASSETS DEPRECIATION CAPITAL ASSETS Capital assets are long-lived assets that are used in the operations of a business and are not
Prepared by: Alex Socratous For My High School Students CHAPTER 2 CAPITAL ASSETS DEPRECIATION CAPITAL ASSETS Capital assets are long-lived assets that are used in the operations of a business and are not
Capital Assets. Apply cost principle to compute the cost of capital assets.
 Capital Assets Objectives : Describe capital assets and issues accounting for them. Apply cost principle to compute the cost of capital assets. Amortization methods: straight-line, units-ofproduction,
Capital Assets Objectives : Describe capital assets and issues accounting for them. Apply cost principle to compute the cost of capital assets. Amortization methods: straight-line, units-ofproduction,
Chapter 10: Fixed Assets and Intangible Assets
 Chapter 10: Fixed Assets and Intangible Assets Nature of Fixed Assets Fixed assets are long-term or relatively permanent assets, such as equipment, machinery, buildings, and land. Other descriptive titles
Chapter 10: Fixed Assets and Intangible Assets Nature of Fixed Assets Fixed assets are long-term or relatively permanent assets, such as equipment, machinery, buildings, and land. Other descriptive titles
Depreciation and Depletion
 Principles Depreciation and Depletion Prof.Sherif Sabry Spring 2009 1 Depreciation and Depletion Lecture outline Concept of depreciation What depreciation is not for Depreciation methods Asset impairment
Principles Depreciation and Depletion Prof.Sherif Sabry Spring 2009 1 Depreciation and Depletion Lecture outline Concept of depreciation What depreciation is not for Depreciation methods Asset impairment
STUDY OBJECTIVE 1 CAPITAL ASSETS
 Collaboratively Created Collection of Chapter 10 Content STUDY OBJECTIVE 1 CAPITAL ASSETS Capital Assets are used throughout many cycles of a business and are reused over and over again. These assets are
Collaboratively Created Collection of Chapter 10 Content STUDY OBJECTIVE 1 CAPITAL ASSETS Capital Assets are used throughout many cycles of a business and are reused over and over again. These assets are
EXERCISES: SET B. Exercises: Set B 1
 Exercises: Set B 1 EXERCISES: SET B E9-1B The following expenditures relating to plant assets were made by Laurie Company during the first 2 months of 2014. 1. Paid $5,000 of accrued taxes at time plant
Exercises: Set B 1 EXERCISES: SET B E9-1B The following expenditures relating to plant assets were made by Laurie Company during the first 2 months of 2014. 1. Paid $5,000 of accrued taxes at time plant
TOWN OF LINCOLN COUNCIL POLICY
 Page 1 of 10 PURPOSE The purpose of this policy is to prescribe the accounting treatment for tangible capital assets so that users of the financial report can discern information about the investment in
Page 1 of 10 PURPOSE The purpose of this policy is to prescribe the accounting treatment for tangible capital assets so that users of the financial report can discern information about the investment in
Test Code F1 Branch (MULTIPLE) (Date : )
 FINAL CA May 2018 ACCOUNTING STANDARDS (PART 1) Test Code F1 Branch (MULTIPLE) (Date : 03.12.2017) (50 Marks) compulsory. Note: All questions are Question 1 (5 marks) As per para 10 of AS 2 Valuation of
FINAL CA May 2018 ACCOUNTING STANDARDS (PART 1) Test Code F1 Branch (MULTIPLE) (Date : 03.12.2017) (50 Marks) compulsory. Note: All questions are Question 1 (5 marks) As per para 10 of AS 2 Valuation of
TANGIBLE CAPITAL ASSETS
 Administrative Procedure 535 Background TANGIBLE CAPITAL ASSETS The Division will follow a prescribed procedure to record and manage the tangible capital assets (TCA) owned by the Division. The treatment
Administrative Procedure 535 Background TANGIBLE CAPITAL ASSETS The Division will follow a prescribed procedure to record and manage the tangible capital assets (TCA) owned by the Division. The treatment
PRACTICE QUESTIONS E-1
 PRACTICE QUESTIONS E-1 1. The FMV of the equipment is Rs. 135,000. 2. Three payments are due to the lessor in the amount of Rs. 50,000 per year beginning 12/31/05. An additional sum of Rs. 1,000 is to
PRACTICE QUESTIONS E-1 1. The FMV of the equipment is Rs. 135,000. 2. Three payments are due to the lessor in the amount of Rs. 50,000 per year beginning 12/31/05. An additional sum of Rs. 1,000 is to
Before Class starts.(make sure your name is on all submissions)
 Before Class starts.(make sure your name is on all submissions) Fourth Homework due 10/27(MW) or 10/28(TR) before class. No exceptions. Help session 10/26 1:00-3:30pm in GBS130 Fifth Homework due 11/3(MW)
Before Class starts.(make sure your name is on all submissions) Fourth Homework due 10/27(MW) or 10/28(TR) before class. No exceptions. Help session 10/26 1:00-3:30pm in GBS130 Fifth Homework due 11/3(MW)
MGT401 Mega Quiz File For Final Term By Innocent Prince
 MGT401 Mega Quiz File For Final Term By Innocent Prince Innocentprince47@gmail.com Question # 1: Which of the following type of the business is governed under the Partnership Act 1932 in Pakistan? Sole-Proprietorship
MGT401 Mega Quiz File For Final Term By Innocent Prince Innocentprince47@gmail.com Question # 1: Which of the following type of the business is governed under the Partnership Act 1932 in Pakistan? Sole-Proprietorship
The Cost of Property, Plant, Equipment
 1 The Cost of Property, Plant, Equipment The cost of property, plant, and equipment includes the purchase price of the asset and all expenditures necessary to prepare the asset for its intended use. Land.
1 The Cost of Property, Plant, Equipment The cost of property, plant, and equipment includes the purchase price of the asset and all expenditures necessary to prepare the asset for its intended use. Land.
Plant assets are resources that have
 10-1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Explain the accounting for plant asset expenditures. Plant assets are resources that have physical substance (a definite size and shape), are used in the operations of a business,
10-1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Explain the accounting for plant asset expenditures. Plant assets are resources that have physical substance (a definite size and shape), are used in the operations of a business,
CHAPTER 10 FIXED ASSETS AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
 1. a. Property, plant, and equipment or Fixed assets b. Current assets (merchandise inventory) 2. Real estate acquired as speculation should be listed in the balance sheet under the caption Investments,
1. a. Property, plant, and equipment or Fixed assets b. Current assets (merchandise inventory) 2. Real estate acquired as speculation should be listed in the balance sheet under the caption Investments,
Balance at Retirements Balance at Beginning Additions and End of ($ in thousands) of Year 3 at Cost Transfers Year 3
 CHAPTER 10 Long-Lived Assets and Depreciation 10-1 ShopKo Stores, Inc. (ShopKo) is a leading regional discount store chain operating 109 discount retail stores in 13 states. ShopKo stores carry a wide
CHAPTER 10 Long-Lived Assets and Depreciation 10-1 ShopKo Stores, Inc. (ShopKo) is a leading regional discount store chain operating 109 discount retail stores in 13 states. ShopKo stores carry a wide
Reporting and Analyzing Long-Term Operating Assets. Learning Objectives coverage by question 12, 13, 16, 18
 Chapter 8 Reporting and Analyzing Long-Term Operating Assets Learning Objectives coverage by question Miniexercises Exercises Problems Cases LO1 Describe and distinguish between tangible and intangible
Chapter 8 Reporting and Analyzing Long-Term Operating Assets Learning Objectives coverage by question Miniexercises Exercises Problems Cases LO1 Describe and distinguish between tangible and intangible
Before Class starts.(make sure your name is on all submissions)
 Before Class starts.(make sure your name is on all submissions) March 27 exam conflicts must be resolved before Spring break. Fourth Homework due Thursday 3/6 before class. Fifth Homework due 3/20 before
Before Class starts.(make sure your name is on all submissions) March 27 exam conflicts must be resolved before Spring break. Fourth Homework due Thursday 3/6 before class. Fifth Homework due 3/20 before
Long-Term Assets C AT EDRÁTICO U PR R I O P I EDRAS S EG. S EM
 Long-Term Assets E DWIN R ENÁN MALDONADO C AT EDRÁTICO U PR R I O P I EDRAS S EG. S EM. 2 017-18 Textbook: Financial Accounting, Spiceland This presentation contains information, in addition to the material
Long-Term Assets E DWIN R ENÁN MALDONADO C AT EDRÁTICO U PR R I O P I EDRAS S EG. S EM. 2 017-18 Textbook: Financial Accounting, Spiceland This presentation contains information, in addition to the material
4/10/2012. Long-Lived Assets and Depreciation. Overview of Long-lived Assets. Learning Objectives (LO) Learning Objectives (LO)
 Learning Objectives (LO) CHAPTER Long-Lived Assets and Depreciation 8 After studying this chapter, you should be able to 1. Distinguish a company s expenses from expenditures that it should capitalize
Learning Objectives (LO) CHAPTER Long-Lived Assets and Depreciation 8 After studying this chapter, you should be able to 1. Distinguish a company s expenses from expenditures that it should capitalize
Accounting 1 Instructor Notes
 Accounting 1 Instructor Notes CHAPTER 10 FIXED ASSETS AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS McDonald's was founded in 1955 and the company now has 22,500 restaurants in 122 countries around the world. Approximately 70
Accounting 1 Instructor Notes CHAPTER 10 FIXED ASSETS AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS McDonald's was founded in 1955 and the company now has 22,500 restaurants in 122 countries around the world. Approximately 70
Lecture 8 (Part 1) Depreciation
 Seg2510 Management Principles for Engineering Managers Lecture 8 (Part 1) Depreciation Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 Depreciation Depreciation
Seg2510 Management Principles for Engineering Managers Lecture 8 (Part 1) Depreciation Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 Depreciation Depreciation
SOLUTIONS Learning Goal 19
 S1 Learning Goal 19 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. b However, the double-declining-balance method calculates the depreciation expense on the full asset cost until the final year of use. 5. d Total appraised
S1 Learning Goal 19 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. b However, the double-declining-balance method calculates the depreciation expense on the full asset cost until the final year of use. 5. d Total appraised
Heiwa Real Estate Co., Ltd.
 To the Shareholders of Heiwa Real Estate Co., Ltd. INFORMATION DISCLOSED ON THE INTERNET UPON ISSUING NOTICE CONCERNING THE CONVOCATION OF THE 94th ORDINARY GENERAL SHAREHOLDERS MEETING THE 94th FISCAL
To the Shareholders of Heiwa Real Estate Co., Ltd. INFORMATION DISCLOSED ON THE INTERNET UPON ISSUING NOTICE CONCERNING THE CONVOCATION OF THE 94th ORDINARY GENERAL SHAREHOLDERS MEETING THE 94th FISCAL
Accounting for Tangible Capital Assets
 Accounting for Tangible Capital Assets Date Approved by Board: 2011.11.17 Resolution No.: 11-113 2016.05.19 16-048 Lead Role: CFO Replaces: N/A Last Review Date: N/A Next Review Date: 2019.05.19 Policy
Accounting for Tangible Capital Assets Date Approved by Board: 2011.11.17 Resolution No.: 11-113 2016.05.19 16-048 Lead Role: CFO Replaces: N/A Last Review Date: N/A Next Review Date: 2019.05.19 Policy
CA - INTER LEASING
 CA - INTER LEASING 1.1 LEASING LOS 1 : Introduction Leasing is an important source of medium-term financing or leasing is the process of financing the cost of an asset. It is an arrangement under which
CA - INTER LEASING 1.1 LEASING LOS 1 : Introduction Leasing is an important source of medium-term financing or leasing is the process of financing the cost of an asset. It is an arrangement under which
Financial Accounting. John J. Wild. Sixth Edition. Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Financial Accounting John J. Wild Sixth Edition McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 08 Reporting and Analyzing Long-Term Assets Conceptual Learning
Financial Accounting John J. Wild Sixth Edition McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 08 Reporting and Analyzing Long-Term Assets Conceptual Learning
Intangibles CHAPTER CHAPTER OBJECTIVES. After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to:
 CHAPTER Intangibles CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the accounting alternatives for intangibles. 2. Record the amortization or impairment of intangibles.
CHAPTER Intangibles CHAPTER OBJECTIVES After careful study of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the accounting alternatives for intangibles. 2. Record the amortization or impairment of intangibles.
Financial Accounting Chapter 10: Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles Answer Key
 Supplemental Instruction Handouts Financial Accounting Chapter 10: Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles Answer Key 1. A) Prepare a calculation to show the cost of this machine. $23,500 x 0.02
Supplemental Instruction Handouts Financial Accounting Chapter 10: Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles Answer Key 1. A) Prepare a calculation to show the cost of this machine. $23,500 x 0.02
Fundamental Accounting Principles, Volume 2
 SOLUTIONS MANUAL to accompany Fundamental Accounting Principles, Volume 2 15 th Canadian Edition by Larson/Jensen/Dieckmann Prepared by: Laura Dallas, Kwantlen Polytechnic University Technical checks by:
SOLUTIONS MANUAL to accompany Fundamental Accounting Principles, Volume 2 15 th Canadian Edition by Larson/Jensen/Dieckmann Prepared by: Laura Dallas, Kwantlen Polytechnic University Technical checks by:
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 28
 S1 Learning Goal 28 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. b However, the double-declining-balance method calculates the depreciation expense on the full asset cost until the final year of use. 5. d Total appraised
S1 Learning Goal 28 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. b However, the double-declining-balance method calculates the depreciation expense on the full asset cost until the final year of use. 5. d Total appraised
6. Record the previous transaction assuming the transaction lacks commercial substance.
 Final Exam Review Chapters 10, 11, & 12 Spring 2017 Information and materials have been used from other sources including the textbook: Intermediate Accounting by Keiso 1. On January 1, 2014 the company
Final Exam Review Chapters 10, 11, & 12 Spring 2017 Information and materials have been used from other sources including the textbook: Intermediate Accounting by Keiso 1. On January 1, 2014 the company
CHAPTER 9 PROPERTY, PLANT, AND EQUIPMENT AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
 PROPERTY, PLANT, AND EQUIPMENT AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS 1. a. Property, plant, and equipment or Plant assets b. Current assets (inventory) 2. Real estate acquired as speculation should be listed in the statement
PROPERTY, PLANT, AND EQUIPMENT AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS 1. a. Property, plant, and equipment or Plant assets b. Current assets (inventory) 2. Real estate acquired as speculation should be listed in the statement
IFRS 16 LEASES. Page 1 of 21
 IFRS 16 LEASES OBJECTIVE The objective is to ensure that lessees and lessors provide relevant information in a manner that faithfully represents those transactions. This information gives a basis for users
IFRS 16 LEASES OBJECTIVE The objective is to ensure that lessees and lessors provide relevant information in a manner that faithfully represents those transactions. This information gives a basis for users
Long-lived, Revenue-producing Assets. Expected to Benefit Future Periods
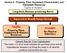 Section 8 - Property, Plant, Equipment (Fixed Assets), and Depletable Resources Types of Assets Long-lived, Revenue-producing Assets 10-1 Expected to Benefit Future Periods Tangible Property, Plant, Equipment
Section 8 - Property, Plant, Equipment (Fixed Assets), and Depletable Resources Types of Assets Long-lived, Revenue-producing Assets 10-1 Expected to Benefit Future Periods Tangible Property, Plant, Equipment
CHAPTER 10 Capital Assets
 CHAPTER 10 Capital Assets ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE Study Objectives Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Set A Problems Set B 1. Distinguish between tangible and intangible capital assets.
CHAPTER 10 Capital Assets ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE Study Objectives Questions Brief Exercises Exercises Problems Set A Problems Set B 1. Distinguish between tangible and intangible capital assets.
New HKFRS for NPO/NGO 16 March 2005
 New HKFRS for NPO/NGO 16 March 2005 HKFRS Nelson Lam CFA FCCA FCPA(Practising) MBA MSc BBA CPA(US) ACA 2006 Nelson 1 Today s Agenda Property, plant and equipment (HKAS 16) Investment property (HKAS 40)
New HKFRS for NPO/NGO 16 March 2005 HKFRS Nelson Lam CFA FCCA FCPA(Practising) MBA MSc BBA CPA(US) ACA 2006 Nelson 1 Today s Agenda Property, plant and equipment (HKAS 16) Investment property (HKAS 40)
On January 4, 2001, Exeter purchased a machine for $48, 120 and it was estimated to have a useful life of six years and a salvage value of $15, 000.
 Review problem : On January 4, 2001, Exeter purchased a machine for $48, 120 and it was estimated to have a useful life of six years and a salvage value of $15, 000. On October 4, 2003, the motor in the
Review problem : On January 4, 2001, Exeter purchased a machine for $48, 120 and it was estimated to have a useful life of six years and a salvage value of $15, 000. On October 4, 2003, the motor in the
B EXERCISES E11-1B (Depreciation Computations SL, SYD, DDB) Instructions (a) (b) (c) E11-2B (Depreciation Conceptual Understanding) Instructions (a)
 B EXERCISES E11-1B (Depreciation Computations SL, SYD, DDB) Vaughn Company purchases equipment on January 1, Year 1, at a cost of $500,000. The asset is expected to have a service life of 10 years and
B EXERCISES E11-1B (Depreciation Computations SL, SYD, DDB) Vaughn Company purchases equipment on January 1, Year 1, at a cost of $500,000. The asset is expected to have a service life of 10 years and
March 23, 2006 Anderson ECON 136A 11am Class FINAL EXAM v. 1 Name
 March 23, 2006 Anderson ECON 136A 11am Class FINAL EXAM v. 1 Name YOU MUST WRITE YOUR NAME ON THIS EXAM AND TURN IT IN WITH YOUR SCANTRON AND BLUE-BOOK! Complete questions #1-25 on your scantron AND WRITE
March 23, 2006 Anderson ECON 136A 11am Class FINAL EXAM v. 1 Name YOU MUST WRITE YOUR NAME ON THIS EXAM AND TURN IT IN WITH YOUR SCANTRON AND BLUE-BOOK! Complete questions #1-25 on your scantron AND WRITE
Peters Township Sanitary Authority Capital Assets
 Peters Township Sanitary Authority Capital Assets Section 1 -Capital Fixed Assets Capital Assets are property, plant and equipment that are in service. They are recorded at cost or estimated historical
Peters Township Sanitary Authority Capital Assets Section 1 -Capital Fixed Assets Capital Assets are property, plant and equipment that are in service. They are recorded at cost or estimated historical
2) All long-term leases should be capitalized in the accounts by the lessee.
 Chapter 18 Leases 1) The principal attribute of finance leases is that the risks and rewards of asset ownership are deemed to remain with the lessor. LO: 18-02 List the criteria for classification of a
Chapter 18 Leases 1) The principal attribute of finance leases is that the risks and rewards of asset ownership are deemed to remain with the lessor. LO: 18-02 List the criteria for classification of a
Depreciation of Property and Amortization of Leasehold Improvements
 Statutory Issue Paper No. 67 Depreciation of Property and Amortization of Leasehold Improvements STATUS Finalized March 16, 1998 Original SSAP and Current Authoritative Guidance: SSAP No. 19 Type of Issue:
Statutory Issue Paper No. 67 Depreciation of Property and Amortization of Leasehold Improvements STATUS Finalized March 16, 1998 Original SSAP and Current Authoritative Guidance: SSAP No. 19 Type of Issue:
ACC100 Introduction to Accounting
 ACC100 Introduction to Accounting Week 7 Non-Current Assets: Acquisition and Depreciation Chapter 14 Non-Current Assets: Acquisition and depreciation Study Group Australia Pty Limited, SGA1286-F2/10/12
ACC100 Introduction to Accounting Week 7 Non-Current Assets: Acquisition and Depreciation Chapter 14 Non-Current Assets: Acquisition and depreciation Study Group Australia Pty Limited, SGA1286-F2/10/12
Chapter 11 Depreciation. Depreciations: Straight Line Sum of Years Digits Declining Balance
 Chapter 11 Depreciation Depreciations: Straight Line Sum of Years Digits Declining Balance 1 Depreciation is important because it affects the taxes that firms pay. The taxable income is (Income expenses).
Chapter 11 Depreciation Depreciations: Straight Line Sum of Years Digits Declining Balance 1 Depreciation is important because it affects the taxes that firms pay. The taxable income is (Income expenses).
IFRS Training. IAS 38 Intangible Assets. Professional Advisory Services
 IFRS Training IAS 38 Intangible Assets Table of Contents Section 1 Overview 2 Introduction to Intangible Assets 3 Recognition and Initial Measurement 4 Internally Generated Intangible Assets 5 Measurement
IFRS Training IAS 38 Intangible Assets Table of Contents Section 1 Overview 2 Introduction to Intangible Assets 3 Recognition and Initial Measurement 4 Internally Generated Intangible Assets 5 Measurement
Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets
 10 Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets Learning Objectives 1 Explain the accounting for plant asset expenditures. 2 Apply depreciation methods to plant assets. 10-1 3 4 5 Explain how
10 Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets Learning Objectives 1 Explain the accounting for plant asset expenditures. 2 Apply depreciation methods to plant assets. 10-1 3 4 5 Explain how
FINANCE. Tangible Capital Assets are non-financial assets having physical substance that:
 EMC Reviewed: November 5, 2013 Policy Council Review: First Reading: November 4, 2013 Board Approved December 10, 2013: BM # 14:2013-2014 EMC Reviewed May 15, 2017 Board Approved June 22, 2017 BM# 46:
EMC Reviewed: November 5, 2013 Policy Council Review: First Reading: November 4, 2013 Board Approved December 10, 2013: BM # 14:2013-2014 EMC Reviewed May 15, 2017 Board Approved June 22, 2017 BM# 46:
CHAPTER 7. Depreciation And Income Taxes. Created By : Eng.Maysa Gharaybeh
 CHAPTER 7 Depreciation And Income Taxes Created By : Eng.Maysa Gharaybeh Depreciation Decrease in value of physical properties with passage of time and use. More specifically: Accounting concept establishing
CHAPTER 7 Depreciation And Income Taxes Created By : Eng.Maysa Gharaybeh Depreciation Decrease in value of physical properties with passage of time and use. More specifically: Accounting concept establishing
Chapter 10 Capital Assets Solutions. (g) NA (current asset) (h) NR (i) NA (inventory) (j) I (k) I (l) NA (investment) (m) NR (n) NR (o) NR (p) I
 Chapter 10 Capital Assets Solutions Assigned Questions: Study Objective Textbook Pages to Read 9 p. 481-486 19 14-10 Solutions: Q1. Tangible and intangible capital assets both are long-lived assets that
Chapter 10 Capital Assets Solutions Assigned Questions: Study Objective Textbook Pages to Read 9 p. 481-486 19 14-10 Solutions: Q1. Tangible and intangible capital assets both are long-lived assets that
Accounting for Leases
 Office: Business Services Procedure Contact: Director of Business Services Related Policy or Policies: Noted within procedure statement Revision History Revision Number: Change: Date: 001 Update content
Office: Business Services Procedure Contact: Director of Business Services Related Policy or Policies: Noted within procedure statement Revision History Revision Number: Change: Date: 001 Update content
Policy Title ACCOUNTING FOR TANGIBLE CAPITAL ASSETS
 Department Administration ACCOUNTING FOR TANGIBLE CAPITAL ASSETS Date: October 13, 2011 1 of 6 Resolution No. C/627/11 Policy Statement: This policy prescribes the accounting treatment for tangible capital
Department Administration ACCOUNTING FOR TANGIBLE CAPITAL ASSETS Date: October 13, 2011 1 of 6 Resolution No. C/627/11 Policy Statement: This policy prescribes the accounting treatment for tangible capital
Work4Me Accounting Simulations. Problem Fourteen
 Work4Me Accounting Simulations 3 rd Web-Based Edition Problem Fourteen Plant Acquisition and Disposal Page 1 INTRODUCTION The Deco-Block Company buys decorative pre-cast cement blocks for retaining walls
Work4Me Accounting Simulations 3 rd Web-Based Edition Problem Fourteen Plant Acquisition and Disposal Page 1 INTRODUCTION The Deco-Block Company buys decorative pre-cast cement blocks for retaining walls
SCHOOL DISTRICT FIXED ASSET POLICY
 ADMINISTRATION 7.0 POLICY 7.33 The Centennial School Board recognizes the importance of maintaining a comprehensive capital asset inventory. The Superintendent shall be responsible for implementing this
ADMINISTRATION 7.0 POLICY 7.33 The Centennial School Board recognizes the importance of maintaining a comprehensive capital asset inventory. The Superintendent shall be responsible for implementing this
Series: Capital Investments How to Calculate Straight-line Depreciation
 Series: Capital Investments How to Calculate Straight-line Table of Contents The Straight-Line Method... 2 An Example of How to Calculate Straight-line... 2 Practice How to Calculate Straight-line... 4
Series: Capital Investments How to Calculate Straight-line Table of Contents The Straight-Line Method... 2 An Example of How to Calculate Straight-line... 2 Practice How to Calculate Straight-line... 4
County of Monterey. Capital Asset Policy
 County of Monterey Capital Asset Policy Office of the Auditor-Controller 168 W. Alisal Street Salinas, California Effective December 11, 2007 [Version November 16, 2007] County of Monterey Capital Asset
County of Monterey Capital Asset Policy Office of the Auditor-Controller 168 W. Alisal Street Salinas, California Effective December 11, 2007 [Version November 16, 2007] County of Monterey Capital Asset
Depreciation - amortization of property, plant, and equipment. Depletion - amortization of mineral resource properties
 Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) - include long-term resources such as office, factory, and warehouse buildings, investment property, equipment (machinery, furniture, tools), mineral resource properties
Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) - include long-term resources such as office, factory, and warehouse buildings, investment property, equipment (machinery, furniture, tools), mineral resource properties
International Financial Reporting Standard 16 Leases. Objective. Scope. Recognition exemptions (paragraphs B3 B8) IFRS 16
 International Financial Reporting Standard 16 Leases Objective 1 This Standard sets out the principles for the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of leases. The objective is to ensure
International Financial Reporting Standard 16 Leases Objective 1 This Standard sets out the principles for the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of leases. The objective is to ensure
Plant design and economics (8)
 Plant design and economics (8) Zahra Maghsoud ٢ DEPRECIATION (Ch. 9 Peters and Timmerhaus ) The reduction in value due to physical deterioration, technological advances, economic changes, or other factors
Plant design and economics (8) Zahra Maghsoud ٢ DEPRECIATION (Ch. 9 Peters and Timmerhaus ) The reduction in value due to physical deterioration, technological advances, economic changes, or other factors
Accounting B LECTURE 1: NON-CURRENT ASSETS. Recording, expensing and reporting non-current assets
 Accounting B LECTURE 1: NON-CURRENT ASSETS Recording, expensing and reporting non-current assets - Asset: a resource controlled by an entity because of past events and from which future economic benefits
Accounting B LECTURE 1: NON-CURRENT ASSETS Recording, expensing and reporting non-current assets - Asset: a resource controlled by an entity because of past events and from which future economic benefits
Supplemental Instruction Handouts Financial Accounting Chapter 9: Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles Answer Key
 Supplemental Instruction Handouts Financial Accounting Chapter 9: Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles Answer Key 1. A) Prepare a calculation to show the cost of this machine. $23,500 x 0.02 =
Supplemental Instruction Handouts Financial Accounting Chapter 9: Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles Answer Key 1. A) Prepare a calculation to show the cost of this machine. $23,500 x 0.02 =
Adopted: November 2013 MSBA/MASA Model Policy 704 Orig Revised: May 2015 Rev. 2009
 Adopted: November 2013 MSBA/MASA Model Policy 704 Orig. 1995 Revised: May 2015 Rev. 2009 704 DEVELOPMENT AND MAINTENANCE OF AN INVENTORY OF FIXED ASSETS AND A FIXED ASSET ACCOUNTING SYSTEM I. PURPOSE The
Adopted: November 2013 MSBA/MASA Model Policy 704 Orig. 1995 Revised: May 2015 Rev. 2009 704 DEVELOPMENT AND MAINTENANCE OF AN INVENTORY OF FIXED ASSETS AND A FIXED ASSET ACCOUNTING SYSTEM I. PURPOSE The
GASBs Presented by: William Blend, CPA, CFE
 GASBs 87-89 Presented by: William Blend, CPA, CFE Leases: Statement 87 Effective Date and General Implementation Effective for Florida fiscal year end 2021. Earlier application is encouraged. Leases should
GASBs 87-89 Presented by: William Blend, CPA, CFE Leases: Statement 87 Effective Date and General Implementation Effective for Florida fiscal year end 2021. Earlier application is encouraged. Leases should
Accounting Standards for Enterprises No Leases No. 3 [2006] of the Ministry of Finance
![Accounting Standards for Enterprises No Leases No. 3 [2006] of the Ministry of Finance Accounting Standards for Enterprises No Leases No. 3 [2006] of the Ministry of Finance](/thumbs/76/73123969.jpg) Accounting Standards for Enterprises No. 21 - Leases No. 3 [2006] of the Ministry of Finance Chapter I General Provisions Article 1With a view to regulating the recognition and measurement of leases, as
Accounting Standards for Enterprises No. 21 - Leases No. 3 [2006] of the Ministry of Finance Chapter I General Provisions Article 1With a view to regulating the recognition and measurement of leases, as
Non-current Assets. Prof.(FH) Dr. Walter Egger
 Non-current Assets Prof.(FH) Dr. Walter Egger IAS 38 Intangible Assets Intangible Asset Is an identifiable non-monetary asset without physical substance Identifiability Seperable (can be seperated, divided
Non-current Assets Prof.(FH) Dr. Walter Egger IAS 38 Intangible Assets Intangible Asset Is an identifiable non-monetary asset without physical substance Identifiability Seperable (can be seperated, divided
Distinctive Financial Reporting
 Distinctive Financial Reporting FAC3702 Study unit 4 Intangible assets Overview Terminology Recognition & initial measurement of intangible assets Cost of internally generated intangible asset Recognition
Distinctive Financial Reporting FAC3702 Study unit 4 Intangible assets Overview Terminology Recognition & initial measurement of intangible assets Cost of internally generated intangible asset Recognition
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 MARCH 2017
 4 PARTICULARS OF INCOME AND EXPENDITURE FROM SOCIAL HOUSING LETTINGS Housing accom Care and supported Temporary accom Rent receivable 114,855 16,847 9,659 1,081 142,442 141,633 Service charges 6,288 6,620
4 PARTICULARS OF INCOME AND EXPENDITURE FROM SOCIAL HOUSING LETTINGS Housing accom Care and supported Temporary accom Rent receivable 114,855 16,847 9,659 1,081 142,442 141,633 Service charges 6,288 6,620
What makes a lease a lease?
 Leases What makes a lease a lease? 2 3 Lease? Customer enters into a contract with a ship owner to transport its cargo The contract specifies the cargo to be transported on the ship and the dates of pickup
Leases What makes a lease a lease? 2 3 Lease? Customer enters into a contract with a ship owner to transport its cargo The contract specifies the cargo to be transported on the ship and the dates of pickup
To download more slides, ebook, solutions and test bank, visit CHAPTER 21 ACCOUNTING FOR LEASES
 CHAPTER 21 ACCOUNTING FOR LEASES IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter. TRUE-FALSE Conceptual Answer No. Description T 1. Benefits of leasing. F 2. Accounting for long-term leases. F
CHAPTER 21 ACCOUNTING FOR LEASES IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter. TRUE-FALSE Conceptual Answer No. Description T 1. Benefits of leasing. F 2. Accounting for long-term leases. F
CA. Gopal Ji Agrawal
 CA. Gopal Ji Agrawal 1. Scope 2. Key concepts 3. Accounting for leases 4. Other Lease Contracts 4. Disclosure 5. Appendix (s) 6. Questions October 1980 September 1982 IAS 17 Accounting for Leases Exposure
CA. Gopal Ji Agrawal 1. Scope 2. Key concepts 3. Accounting for leases 4. Other Lease Contracts 4. Disclosure 5. Appendix (s) 6. Questions October 1980 September 1982 IAS 17 Accounting for Leases Exposure
